For Big dreams, You don’t need big fees. Get 20% Off on all courses
| Grab 20% offer soon!
For Big dreams, You don’t need big fees. Get 20% Off on all courses
| Grab 20% offer soon!
Let’s start with a few sentences that highlight commonly confused words in English. Read these aloud!
The effect of the new medicine was to affect the patient’s mood positively.
The stationary bike in the gym was covered in dust, while the new stationery was not.
The loose dog ran around the park, and I hope I don’t lose sight of it.
You may find yourself stuck in a loop of puzzlement! But fret not! Even proficient speakers occasionally use the incorrect term when they mean another, ignoring the fact that these words often confused all have different meanings. There are lots of English confusing words that can be perplexing because, although they may sound the same, they change when you spell them or get their meaning.
Before delving deeper into confusable words, let’s explore the types of confusion words that often trip us up:
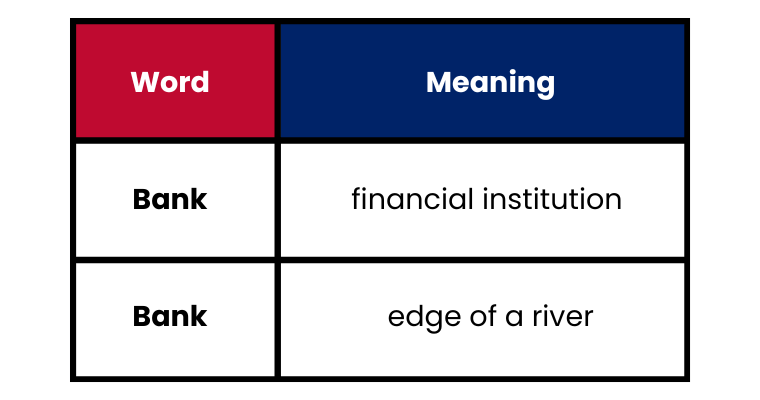
2. Homonyms: These are words that have the same spelling and pronunciation but different meanings.
Words like,

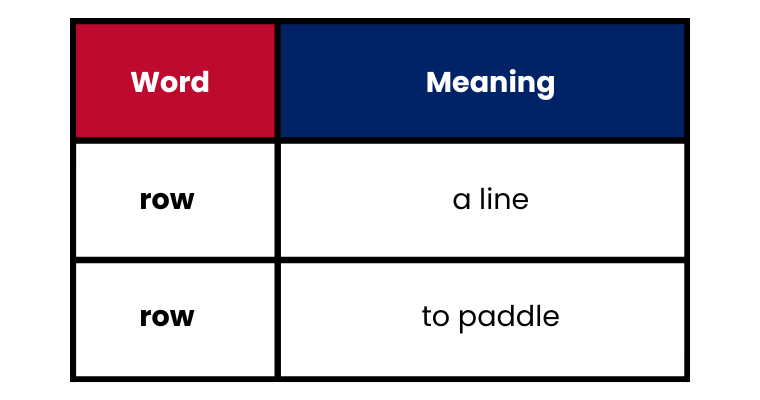
3. Homographs: These are words that have the same spelling but different pronunciations and meanings.
Examples:

Accept – to receive or agree to something.
Except – excluding or leaving out.
Words can be tricky little things, can’t they? Let’s untangle some common word pairs that often get tangled up: allusion vs. illusion, complement vs. compliment, desert vs. dessert, and emigrate vs. immigrate. Now, let’s explore the differences and learn more.
Here’s a list of words often confused examples that you should familiarize yourself with:
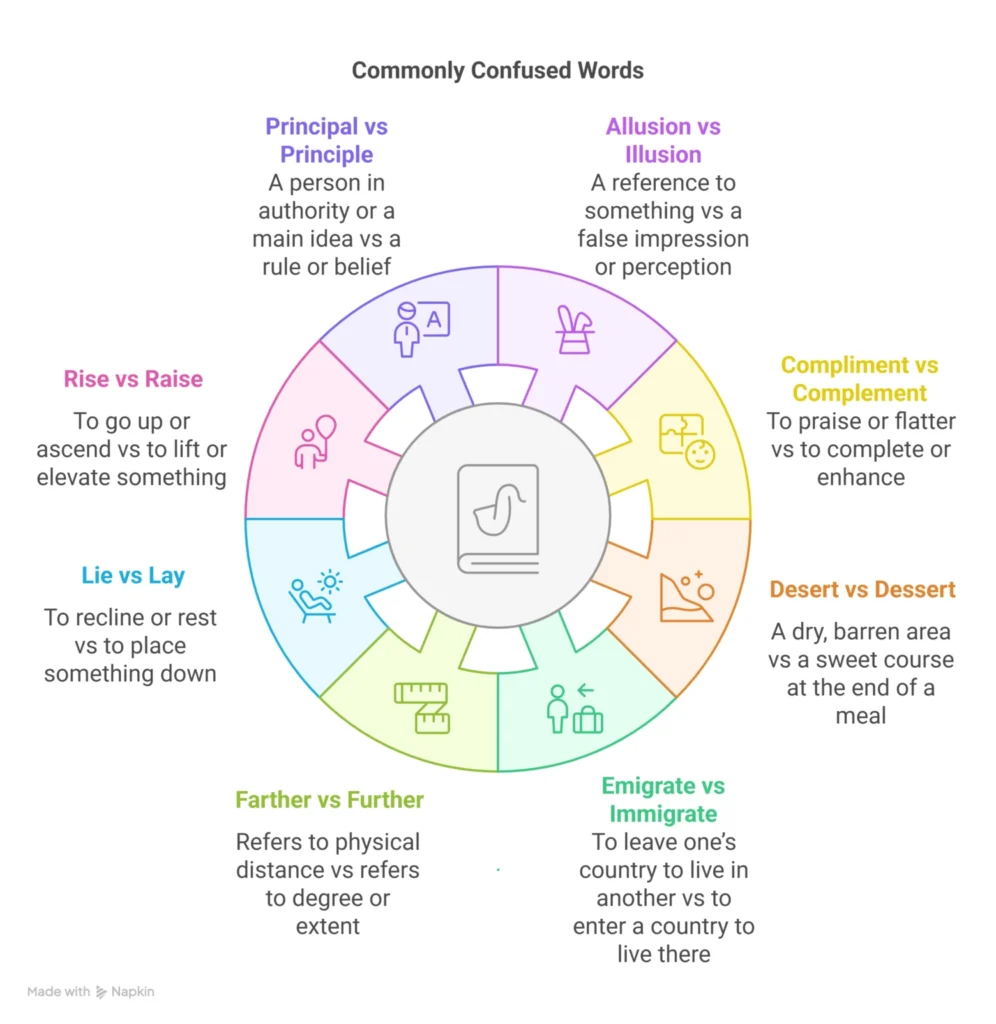
Allusion: A reference to something.
Illusion: A false impression or perception.
Compliment: To praise or flatter.
Complement: To complete or enhance.
Desert: A dry, barren area.
Dessert: A sweet course at the end of a meal.
Emigrate: To leave one’s country to live in another.
Immigrate: To enter a country to live there.
Farther: Refers to physical distance.
Further: Refers to degree or extent.
Lie: To recline or rest.
Lay: To place something down.
Rise: To go up or ascend.
Raise: To lift or elevate something.
Principal: A person in authority or a main idea.
Principle: A rule or belief.
By understanding the nuances of these commonly confused words, you can elevate your writing and speaking skills. Let’s explore some more confusing word pairs:
Assure: To convince someone of something.
Ensure: To make sure something happens.
Capital: The city of a state or nation, or wealth.
Capitol: A building where a legislature meets.
Conscious: Aware of and responding to one’s surroundings.
Conscience: A sense of right and wrong.
Discreet: Careful and prudent.
Discrete: Separate and distinct.
Elicit: To draw out or evoke.
Illicit: Illegal or forbidden.
Council: A group of people meeting together for a specific purpose.
Counsel: Advice or guidance.
Appraise: To assess or evaluate.
Apprise: To inform or notify.
Words are the building blocks of language, and understanding their nuances can significantly enhance our communication. In this blog, we’ve explored some common English words that often cause confusion. By grasping the subtle differences between these words, we can express ourselves with greater precision and clarity.
Its vs. It’s: Possessive pronoun vs. contraction of “it is”
Than vs. Then: Comparison vs. time or sequence
Your vs. You’re: Possessive pronoun vs. contraction of “you are”
To vs. Too vs. Two: Preposition, also/excessive, or the number 2
There vs. Their vs. They’re: Location, possession, or contraction of “they are”
Lose vs. Loose: To misplace or fail to win vs. not tight
Passed vs. Past: Moved beyond vs. previous time or place
Set vs. Sit: To place or arrange vs. to be seated
Preethi is a results-driven content creator and copywriter who turns ideas into powerful words. With a knack for engaging storytelling and SEO-savvy writing, she helps brands connect, convert, and grow.

English is a language that has evolved over centuries, borrowing from various sources. This rich history has led to many words with similar sounds or spellings but different meanings.
Affect: This is usually a verb that means to influence or impact something.
E.g., “The rain will affect our picnic
Effect: This is typically a noun that means a result or outcome.
Eg: The effect of the rain was a cancelled picnic.
Read widely: Expose yourself to diverse writing styles and vocabulary.
Write regularly: Practice makes perfect.
Use a dictionary and thesaurus: These tools can help you find the right word and avoid common mistakes.
Proofread carefully: Check your work for errors in grammar, punctuation, and word usage.
A strong thesis statement should be clear, concise, and arguable. It should state the main idea of your essay and provide a roadmap for your argument.
Noun: A person, place, thing, or idea. (e.g., book, table, love, happiness)
Verb: An action word. (e.g., run, jump, think, feel)